One of the fundamental decisions to make when determining the architecture of a system is to determine if communications will be synchronous or asynchronous.
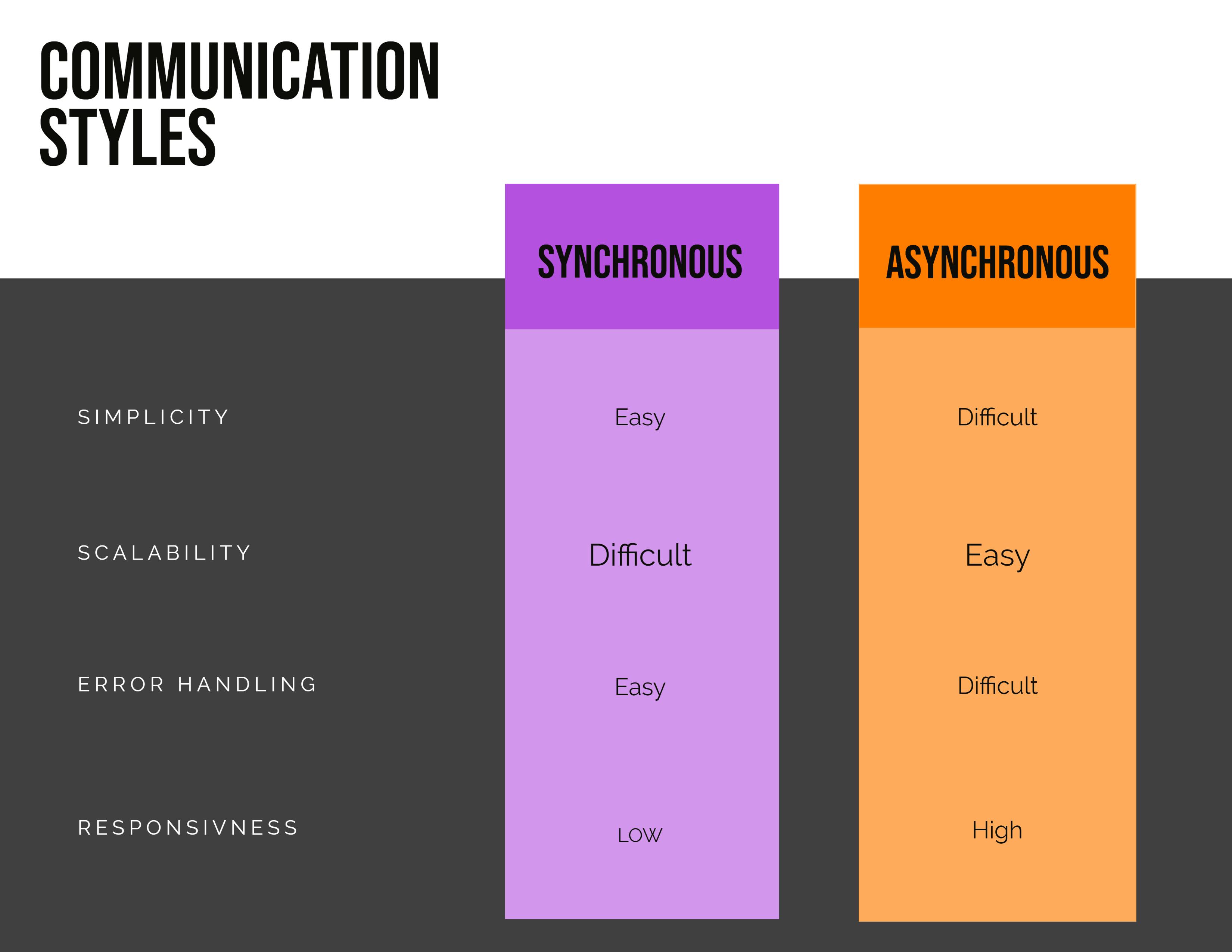
Each communication style offers a set of trade-offs, however, synchronous communication does not present as many challenges as asynchronous communication, making it the preferred default communication mode.
“𝘜𝘴𝘦 𝘴𝘺𝘯𝘤𝘩𝘳𝘰𝘯𝘰𝘶𝘴 𝘣𝘺 𝘥𝘦𝘧𝘢𝘶𝘭𝘵, 𝘢𝘴𝘺𝘯𝘤𝘩𝘳𝘰𝘯𝘰𝘶𝘴 𝘸𝘩𝘦𝘯 𝘯𝘦𝘤𝘦𝘴𝘴𝘢𝘳𝘺.” – Michael Richards & Neal Ford
𝐒𝐲𝐧𝐜𝐡𝐫𝐨𝐧𝐨𝐮𝐬 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐦𝐮𝐧𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧:
Simplicity is of greater strength within synchronous communications as it does not present many of the challenges brought about by asynchronous communications.
Scalability is more challenging to achieve when synchronous communication is utilized, as different components may not be able to manifest different characteristics, for example, if one component is much more scalable than another it interacts with then this may create a performance bottleneck on the lesser scalable component leading to timeouts, this in turn compromises reliability.
𝐀𝐬𝐲𝐧𝐜𝐡𝐫𝐨𝐧𝐨𝐮𝐬 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐦𝐮𝐧𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧:
Responsiveness is a positive side effect of the fire-and-forget nature of asynchronous calls, one component may submit information to another without relying on an immediate outcome of an operation, for example, an end user may submit a comment on a social media platform and not have to wait for it to pass through multiple processors rather they may simply be presented with an acknowledgment of their submission.
Error handling complexity is increased as fire-and-forget calls do not immediately return the outcome of an invoked operation, making it more challenging to feedback failure to users, fortunately, error handling techniques such as the Workflow Event pattern can be leveraged to mitigate error handling shortcomings.
Data loss risk is heightened, data may flow from one component to another prior to reaching its final destination, and problems may occur during the processing of data by a component or within transmission via a communication channel, this risk can be mitigated by utilizing techniques such as the Client Acknowledge Mode and Last Participant Support techniques.
It can be possible to achieve synchronous-like communication in an asynchronous system by leveraging request-reply or pseudo-synchronous messaging.
Certain architectural choices can enforce a messaging requirement, for example, only asynchronous messaging can be supported in event-driven architectures.